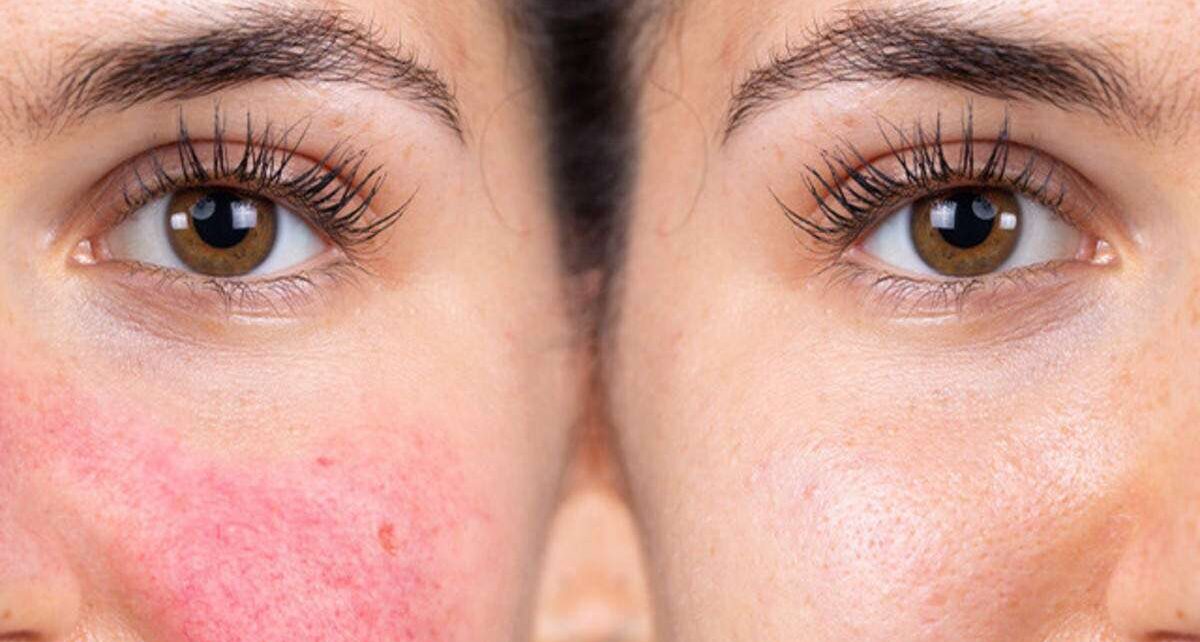
Rosacea is a inflammatory and chronic skin condition that mainly affects the face. It is characterized by redness, flushing, visible blood vessels (telangiectasia), and in some cases, the development of small, pus-filled, red bumps or pustules.
Rosacea typically appears on the central portion of the face, including the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin.
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of 玫瑰痤瘡can vary from person to person, and the condition may progress in stages.
Here are the common signs and symptoms associated with rosacea:
Facial Redness
Persistent facial redness is a hallmark symptom of rosacea. It typically appears as a flushed or blushed appearance on the central part of the face, including the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin. The redness may come and go or persist for long periods.
Flushing
Many individuals with rosacea experience episodes of facial flushing. Flushing is characterized by a sudden and temporary increase in redness and warmth on the face.
Triggers for flushing can vary, but commonly include exposure to heat, sunlight, spicy foods, alcohol, and emotional stress to 敏感肌
Visible Blood Vessels
Over time, small blood vessels (telangiectasia) may become visible on the surface of the skin. These blood vessels appear as thin, red lines or patterns and are more commonly seen on the cheeks and nose.
Papules and Pustules
In some cases, rosacea may lead to the development of small, red, and pus-filled bumps or pustules on the affected areas of the face. These bumps can resemble acne, but are not caused by the same factors.
Thickened Skin
In advanced cases of rosacea, the skin on the nose may become thickened and enlarged, a condition known as rhinophyma. Rhinophyma is more common in men than in women and is often associated with severe, longstanding rosacea.
Eye Irritation
Ocular symptoms can occur in individuals with rosacea. These may include dryness, burning or stinging sensation, redness, itching, sensitivity to light, and the feeling of having a foreign object in the eye. Ocular rosacea requires prompt medical attention.
Treatment
There are various treatment options available for managing the symptoms of rosacea. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the specific symptoms experienced by the individual.
It is best to consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and to determine the most suitable treatment plan.
Here are some common treatment approaches for rosacea:
Topical Medications
Prescription creams, gels, or lotions containing ingredients such as metronidazole, azelaic acid, ivermectin, or brimonidine can help reduce redness, inflammation, and the appearance of bumps and pustules associated with rosacea.
Oral Medications
In some cases, oral antibiotics, such as tetracycline, doxycycline, or minocycline, may be prescribed to control inflammation and reduce symptoms. Isotretinoin, a potent oral medication, may be considered for severe cases of rosacea that do not respond to other treatments.
Laser and Light Therapy
Laser M22 and light-based therapies can be effective in reducing the appearance of visible blood vessels, redness, and thickened skin.
These treatments target specific blood vessels or pigment in the skin, promoting their removal or reduction.
Ocular Treatments
If rosacea affects the eyes, a doctor may prescribe eye drops or ointments to alleviate symptoms such as dryness, inflammation, and irritation. Proper eyelid hygiene may also be recommended.
Lifestyle Modifications
Certain lifestyle changes can help manage rosacea symptoms and prevent flare-ups. These may include avoiding triggers such as sunlight, hot or cold weather, spicy foods, alcohol, and stress.
Gentle skincare practices, using mild cleansers and moisturizers suitable for sensitive skin, are also recommended.
Redness-Reducing Techniques
Certain techniques, such as camouflage makeup or green-tinted moisturizers, can help mask facial redness temporarily.
However, it is important to choose products that are non-comedogenic (do not clog pores) and do not irritate the skin further.